Insolvency & Bankruptcy Code, 2016
The concepts of Insolvency and Bankruptcy
When an entity or organization is not capable to assemble its unsettled financial debt towards its lender, thereafter such a situation is referred as Insolvency. Insolvency can be settled by modifying the plan of repayment. In addition, a part of that loan can be written off as well. In case, such a problem is not resolved, a lawsuit may be filed against the insolvent along with the assets, which will be put up for auction to pay off the unsettled debts. An official assignee and/or liquidator are selected by the Government of India, recognize the assets and there after assign it amid the creditors of the insolvent. The concept of bankruptcy refers to a situation when an individual willingly pronounces himself as an insolvent, and proceeds to the court. When the court pronounces the individual as ‘bankrupt’, the court may confiscate the individual property of the insolvent and hand over to its creditors. It offers a fresh charter of existence to the insolvent.
History of Indian Economy
As per the statistics, India’s entire substandard debts amount to 11 percent of the total credit and it is on the rise. Indian economy takes more time to resolve insolvency in comparison to other economies. In case of corporate, substandard debts constitute 56 percent of the total bad debts of state-owned banks. Thousands of litigations are pending demanding retrieval of money. Currently, various jurisdictions of a range of laws are governing insolvency resolution and courts. In the past, there were about 12 laws in relation to insolvency. Past records have indicated that it takes normally 4 years to shut down a company in India. India lacks suitable institutional and permissible apparatus as per as universal standards to deal with debt defaults. As per as the Contracts Act or individual laws such as the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002 or Recovery of Debts Due to Banks and Financial Institutions Act, 1993 failed to give satisfactory outcomes for recovery proceedings by creditors. Moreover, accomplishment by the Sick Industrial Companies (Special Provisions) Act, 1985 (SICA) or the winding up provisions of the Companies Act, 1956 failed to have a significant impact on the process of successful recovery of exceptional debt, nor restructuring of debts. The Presidency Towns Insolvency Act, 1909 and the Provincial Insolvency Act, 1920, are not satisfactory as well. Henceforth, the Government replaced the pre-existing insolvency laws. Now there is only one merged and comprehensive law that will aid easy and time-bound shutting down of business. The Rajya Sabha on 11th May 2016 sanctioned the most important Economic Reform Bill created by the Government known as the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016. The Bill was passed by the Lok Sabha on 5th May 2016. The President gave a nod to the Bill on 28th May 2016.
What is the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016?
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 aspire to combine and modify the regulation related to insolvency declaration of companies and limited liability organization, companies and individuals, into a solitary legislation.
- This legislation focuses on providing restoration and declaration at one time to maximize the value of debtor’s assets.
- The Code enables sick companies to either bring to an end their business or create a restoration plan, or aid the investors to exit.
- In addition, the Code sanctions the operational creditors such as workmen, suppliers and so on to begin the insolvency resolution process in situations where default takes place.
- The Code does not make any difference between the rights of international as well as domestic creditors. Furthermore, no difference can be spotted between the divisions of financial institutions as well.
- The Code maintains the benefit of all the stakeholders. These are subjected to modification as per as the priority of payment of Government dues.
The legislators are determined to introduce regulations matching the international standard, which follows the unique philosophy that insolvency resolution must be commercially as well as professionally based instead of court-driven. However, the role of authorities providing judgment is inadequate as it fails to ensure the due process. Instead, it focuses on adjudicating on the virtues of the insolvency resolution. The Code revokes the Presidency Towns Insolvency Act, 1909, and Provincial Insolvency Act, 1920. Furthermore, it altered 11 legislation. These are as follows:
- Indian Partnership Act, 1932
- The Companies Act, 2013
- Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008,
- Sick Industrial Companies (Special Provisions) Repeal Act, 2003
- Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002
- The Code has an over ruling effect over all other laws to steer clear of any further proceedings in insolvency proceedings. Civil courts as well as authority do not have the authority and cannot permit any command.
- The Code is a modified law. It replaces over various regulations. Such a law, when put into practice shall prove to be a crucial phase in developing the procedure of recovery of bad debts.
- Besides, an economic growth is observed due to the inflexible time frame approved in the Code for resolution of insolvency as well as liquidation proceedings.
What do we mean by Insolvency Resolution Process?
Insolvency Resolution Process refers to the procedure during which financial creditors evaluate the debtor’s business and examines whether the business is practicable. Furthermore, the options for its liberation and restoration are also suggested.
What is Liquidation?
Liquidation refers to a situation when the insolvency resolution process did not succeed. It may also refer to a situation when financial creditors make a decision to shut down and allocate the assets of the debtor. Thus, “Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016” is an interesting addition to the existing regulations. The Code introduced changes which have caused hesitation among people. Furthermore, this Code has projected an enormous refurbishment of laws, measures, and infrastructure. When this Code will be implemented effectively the previous flaws in the law machinery can be easily resolved.





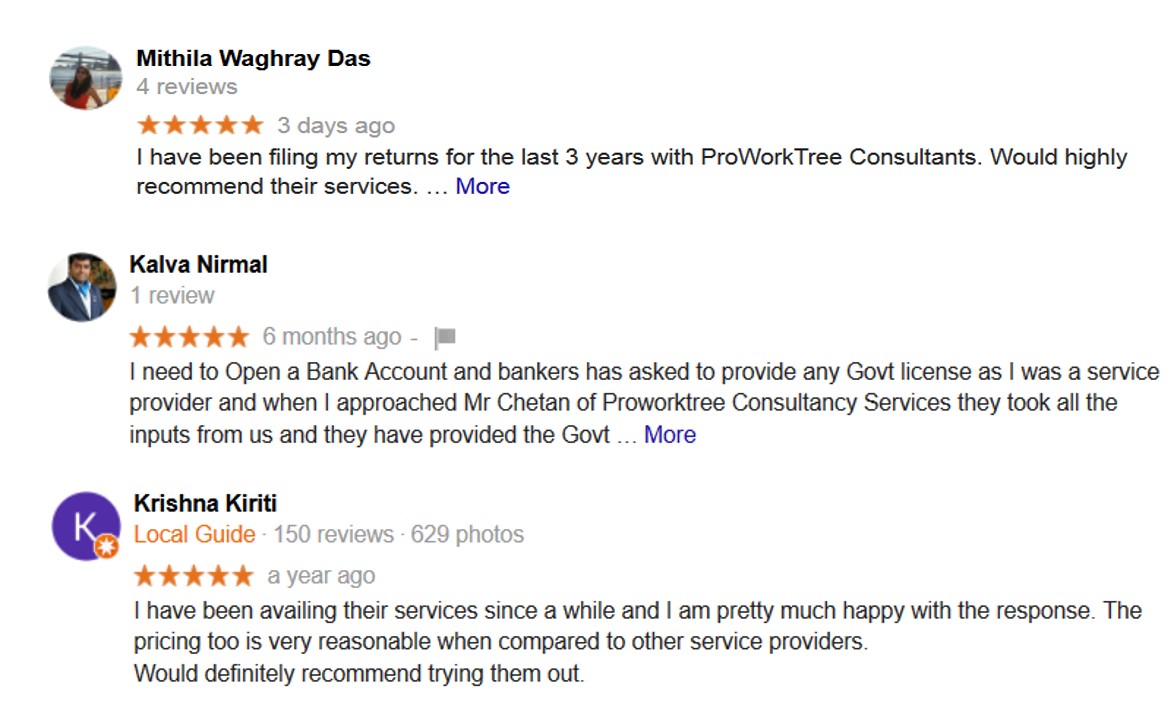
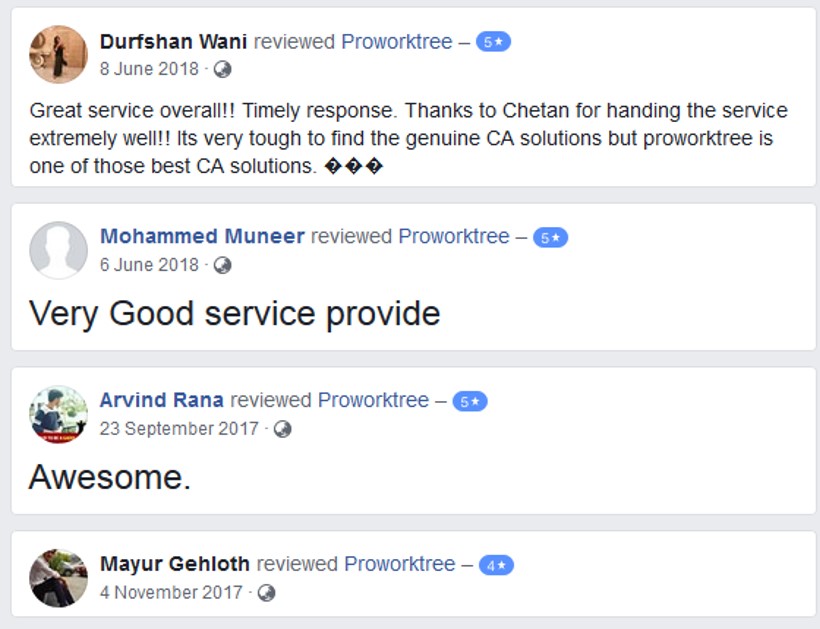
 Corporate Entity Registration
Corporate Entity Registration


0 comments have been posted.